![]()
Love to eat mushroom but not sure if it is ebible? There’s a dataset in Kaggle which can be used to build a model classifying if a mushroom is safe and consumable.
The main goal of this little task is to attempt aswering 2 questions :
- What types of machine learning models perform best on this dataset?
- Which features are most indicative of a poisonous mushroom?
Also, to help people visualizing the performance of the model and its prediction outcome, a simple web application is built after model building.
Part 1 : Raw Data Exploration
Instaed of the conventional way of exploring the raw data with common pandas library, I decided to try an enhanced version of libraray called pandas-profiling. After a quick look on the documentation, I found it was pretty straight forward to generate a nice and comprehensive report covering the key areas of data screening.
After reading in the dataframe (df), just execute simple line of code
import pandas_profiling as pp
pandas_report = pp.ProfileReport(df)
The pandas report is a html file outlining 5 key summaries [ Overview, Variable, Correlation, Missing values, Sample].
Based on the pandas report, I can now check the summarized statistic variable by variable in more details . Here are the observations and preliminary considerations for model building after studying the report :
- ‘vell-type’ was observed to have only 1 unique variable, others with >=2 unique variables, max unique variable at 12
- ‘vell-type’ to be excluded from modelling since it’s a constant value
- ‘stock-root’ was found having special character “?”
- ‘odor’ and ‘gill-color’ were observed to have positive correlation in this preliminary analysis. To verify further.
Part 2 : Data Input Format Transformation
Before working on model bulding, data was transformed into processable format as input to the model. As all variables were categorical data, label encoder was used on the class variable while other variables were transformed using one hot encoder via pd.get_dummies().
Snippet of the transformed data after dropping vell-type column due to constant value as below :
| cap-shape_b | cap-shape_c | cap-shape_f | cap-shape_k | cap-shape_s | cap-shape_x | cap-surface_f | cap-surface_g | cap-surface_s | cap-surface_y | cap-color_b | cap-color_c | cap-color_e | cap-color_g | cap-color_n | cap-color_p | cap-color_r | cap-color_u | cap-color_w | cap-color_y | bruises_f | bruises_t | odor_a | odor_c | odor_f | odor_l | odor_m | odor_n | odor_p | odor_s | odor_y | gill-attachment_a | gill-attachment_f | gill-spacing_c | gill-spacing_w | gill-size_b | gill-size_n | gill-color_b | gill-color_e | gill-color_g | gill-color_h | gill-color_k | gill-color_n | gill-color_o | gill-color_p | gill-color_r | gill-color_u | gill-color_w | gill-color_y | stalk-shape_e | stalk-shape_t | stalk-root_? | stalk-root_b | stalk-root_c | stalk-root_e | stalk-root_r | stalk-surface-above-ring_f | stalk-surface-above-ring_k | stalk-surface-above-ring_s | stalk-surface-above-ring_y | stalk-surface-below-ring_f | stalk-surface-below-ring_k | stalk-surface-below-ring_s | stalk-surface-below-ring_y | stalk-color-above-ring_b | stalk-color-above-ring_c | stalk-color-above-ring_e | stalk-color-above-ring_g | stalk-color-above-ring_n | stalk-color-above-ring_o | stalk-color-above-ring_p | stalk-color-above-ring_w | stalk-color-above-ring_y | stalk-color-below-ring_b | stalk-color-below-ring_c | stalk-color-below-ring_e | stalk-color-below-ring_g | stalk-color-below-ring_n | stalk-color-below-ring_o | stalk-color-below-ring_p | stalk-color-below-ring_w | stalk-color-below-ring_y | veil-color_n | veil-color_o | veil-color_w | veil-color_y | ring-number_n | ring-number_o | ring-number_t | ring-type_e | ring-type_f | ring-type_l | ring-type_n | ring-type_p | spore-print-color_b | spore-print-color_h | spore-print-color_k | spore-print-color_n | spore-print-color_o | spore-print-color_r | spore-print-color_u | spore-print-color_w | spore-print-color_y | population_a | population_c | population_n | population_s | population_v | population_y | habitat_d | habitat_g | habitat_l | habitat_m | habitat_p | habitat_u | habitat_w | class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Based on this transformed dataframe, data was then further splitted into train and test set using split ratio of 0.3
# split data to train and test set
data_train, data_test, label_train, label_test = train_test_split(data, labels, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
A preliminary check on the correlation of all the features to class was also done to have an overview if features were positively or negatively correlated to the target prediction variable class.
# check correlation of features to class
correlation_overview = data_all.corr()['class'].reset_index()
correlation_overview.rename(columns={'index':'features', 'class':'correlation_to_class'}, inplace=True)
df_feature_correlation = correlation_overview.sort_values(by='correlation_to_class', ascending=False)
df_feature_correlation
| features | correlation_to_class | |
|---|---|---|
| 116 | class | 1.000000 |
| 24 | odor_f | 0.623842 |
| 57 | stalk-surface-above-ring_k | 0.587658 |
| 61 | stalk-surface-below-ring_k | 0.573524 |
| 36 | gill-size_n | 0.540024 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 58 | stalk-surface-above-ring_s | -0.491314 |
| 21 | bruises_t | -0.501530 |
| 35 | gill-size_b | -0.540024 |
| 93 | ring-type_p | -0.540469 |
| 27 | odor_n | -0.785557 |
117 rows × 2 columns
Part 3 : Model Building & Performance Check
Since this was a classification problem, 3 different algorithms were chosen to check prediction outcomes and their performance. Models chosen were :
- logistic_regressionCV
- random_forest_classifier
- kneighbors_classifier
To make the entire train and performance check process iterable for 3 chosen models, a function was written to serve this process.
# define few models to train
model_lr = LogisticRegressionCV(random_state=42)
model_rf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)
model_kn = KNeighborsClassifier()
models_name = ['logistic_regressionCV', 'random_forest_classifier', 'kneighbors_classifier']
models = [model_lr, model_rf, model_kn]
def model_building(model, model_name, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test):
"""
Function to train model and output model performance
"""
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_predict = model.predict(X_test)
y_prob_predict = model.predict_proba(X_test)
# save trained model
filename = f'./pretrained_models/saved_model_{model_name}.sav'
joblib.dump(model, filename)
print('\n')
print(colored(model_name, color='red', attrs=['bold']))
print('-'*80)
print('Model Parameters :')
print(model)
print('-'*80)
print('\n')
# To plot confusion matrix
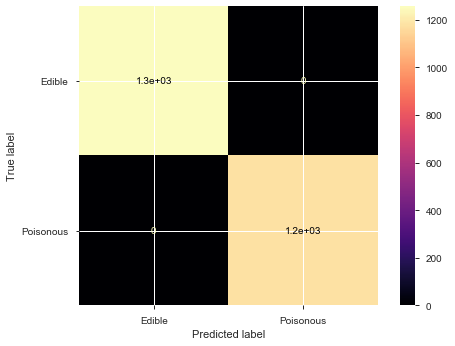
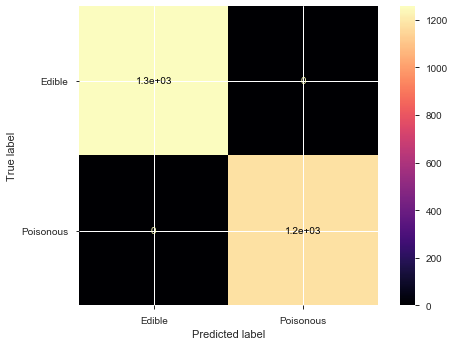
plot_confusion_matrix(model, X_test, y_test, display_labels=['Edible','Poisonous'], cmap='magma')
plt.show(block=False)
# To display classification report showing precision, recall, f1
print('-'*80)
print('Classification report :\n')
print(classification_report(y_test, y_predict))
print('-'*80)
# To plot roc_auc graph to show area under the curve
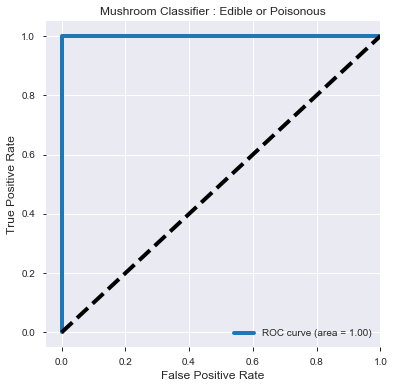
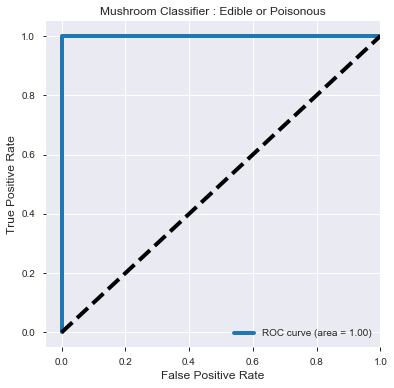
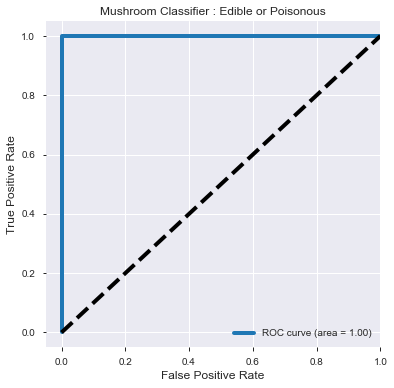
print('ROC_AUC score :')
print(round(roc_auc_score(y_test, y_prob_predict[:,1]),4))
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_test, y_prob_predict[:,1])
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
plt.figure(figsize=[6,6])
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, label='ROC curve (area = %0.2f)' % roc_auc, linewidth=4)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], 'k--', linewidth=4)
plt.xlim([-0.05, 1.0])
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate', fontsize=12)
plt.title('Mushroom Classifier : Edible or Poisonous', fontsize=12)
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()
for i, model in enumerate(models):
model_building(model, models_name[i], data_train, data_test, label_train, label_test)
For an initial trial, default parameters were used for all 3 models. The model performances were found good even with the default parameters.
3.1 Model Performance for Logistic RegressionCV
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Model Parameters :
LogisticRegressionCV(Cs=10, class_weight=None, cv=None, dual=False,
fit_intercept=True, intercept_scaling=1.0, l1_ratios=None,
max_iter=100, multi_class='auto', n_jobs=None,
penalty='l2', random_state=42, refit=True, scoring=None,
solver='lbfgs', tol=0.0001, verbose=0)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Classification report :
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 1257
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 1181
accuracy 1.00 2438
macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 2438
weighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 2438
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ROC_AUC score :
1.0
3.2 Model Performance for Random Forest Classifier
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Model Parameters :
RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, ccp_alpha=0.0, class_weight=None,
criterion='gini', max_depth=None, max_features='auto',
max_leaf_nodes=None, max_samples=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100,
n_jobs=None, oob_score=False, random_state=42, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
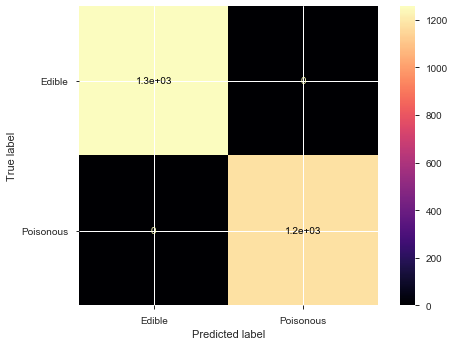
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Classification report :
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 1257
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 1181
accuracy 1.00 2438
macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 2438
weighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 2438
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ROC_AUC score :
1.0
3.3 Model Performance for KNeighbors Classifier
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Model Parameters :
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm='auto', leaf_size=30, metric='minkowski',
metric_params=None, n_jobs=None, n_neighbors=5, p=2,
weights='uniform')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Classification report :
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 1257
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 1181
accuracy 1.00 2438
macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 2438
weighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 2438
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ROC_AUC score :
1.0
Part 4 : Analysis of Feature Importance
To check if there was any variable dominating in predicting the mushroom class and how much the dominance level was, analysis was carried out on the trained models.
4.1 Coefficients derived from Logistic RegressionCV Model
For Logistic RegressionCV, features impact on the model can be extracted by checking the coefficient.
trained_model_lr = joblib.load('./pretrained_models/saved_model_logistic_regressionCV.sav')
# extract feature importance from trained model
feat_importance_lr = trained_model_lr.coef_.tolist()
feat_importance_lr = [round(v, 6) for v in feat_importance_lr[0]]
# set up df for better comparison view
df_feat_importance_lr = pd.DataFrame(data_train.columns, columns=['features'])
df_feat_importance_lr['feature_importance'] = feat_importance_lr
df_feat_importance_lr = df_feat_importance_lr.sort_values('feature_importance', ascending=False)
df_feat_importance_lr
| features | feature_importance | |
|---|---|---|
| 99 | spore-print-color_r | 6.427334 |
| 23 | odor_c | 4.933256 |
| 24 | odor_f | 4.160369 |
| 52 | stalk-root_b | 3.802192 |
| 28 | odor_p | 3.558643 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 100 | spore-print-color_u | -2.710225 |
| 35 | gill-size_b | -3.353126 |
| 25 | odor_l | -4.993461 |
| 22 | odor_a | -5.036676 |
| 27 | odor_n | -6.073253 |
116 rows × 2 columns
To get the top 10 important features, concentation was done to merge the top 5 positive coefficient with top 5 negative coefficient.
df_feat_coef_top10_lr = pd.concat([df_feat_importance_lr.head(5), df_feat_importance_lr.tail(5)])
df_feat_coef_top10_lr.sort_values('feature_importance', ascending=False)
| features | feature_importance | |
|---|---|---|
| 99 | spore-print-color_r | 6.427334 |
| 23 | odor_c | 4.933256 |
| 24 | odor_f | 4.160369 |
| 52 | stalk-root_b | 3.802192 |
| 28 | odor_p | 3.558643 |
| 100 | spore-print-color_u | -2.710225 |
| 35 | gill-size_b | -3.353126 |
| 25 | odor_l | -4.993461 |
| 22 | odor_a | -5.036676 |
| 27 | odor_n | -6.073253 |
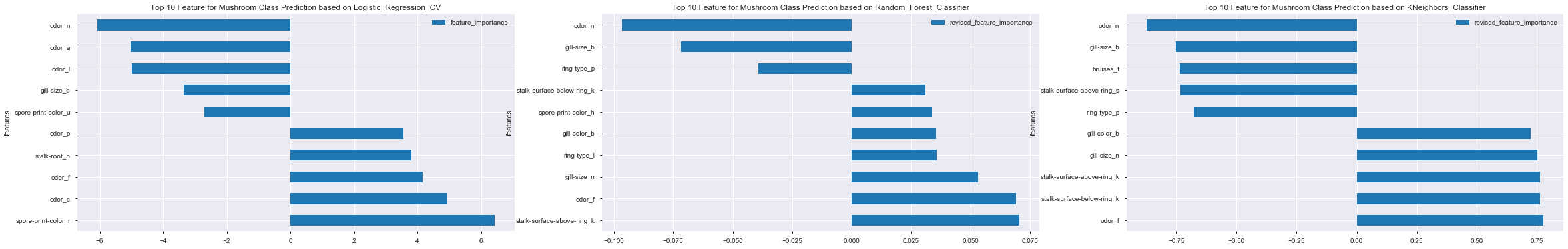
df_feat_coef_top10_lr.plot(x='features', y='feature_importance', kind='barh', figsize=(12,6))
plt.title('Top 10 Feature for Mushroom Class Prediction based on Logistic_Regression_CV')
plt.show()
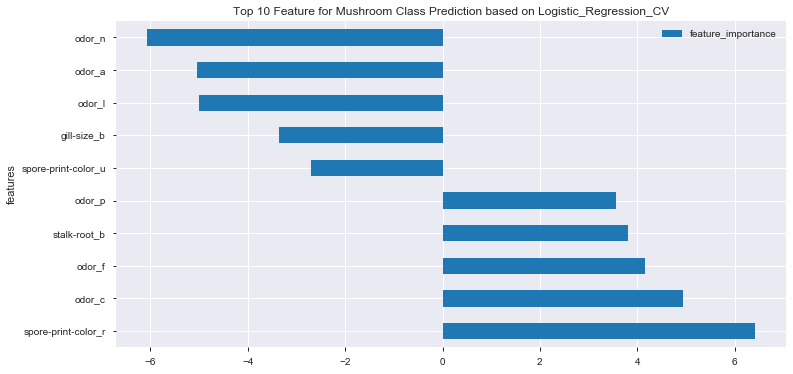
- No particular feature showing dominant effect on mushroom class prediction
- In general, combination of odor, gill-size and spore-print-color demonstrated higher effects on final mushroom class prediction
4.2 Feature Importance derived from Random Forest Classifier Model
Different from Logistic RegressionCV, to identify contributing features, feature importance was extracted out from Random Forest model.
trained_model_rf = joblib.load('./pretrained_models/saved_model_random_forest_classifier.sav')
# extract feature importance from trained model
feat_importance_rf = list(trained_model_rf.feature_importances_)
feat_importance_rf = [round(v, 6) for v in feat_importance_rf]
# set up df for better comparison view
df_feat_importance_rf = pd.DataFrame(data_train.columns, columns=['features'])
df_feat_importance_rf['feature_importance'] = feat_importance_rf
df_feat_importance_rf.sort_values('feature_importance', ascending=False)
| features | feature_importance | |
|---|---|---|
| 27 | odor_n | 0.096636 |
| 35 | gill-size_b | 0.071668 |
| 57 | stalk-surface-above-ring_k | 0.070451 |
| 24 | odor_f | 0.069137 |
| 36 | gill-size_n | 0.053173 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 66 | stalk-color-above-ring_e | 0.000009 |
| 98 | spore-print-color_o | 0.000000 |
| 102 | spore-print-color_y | 0.000000 |
| 94 | spore-print-color_b | 0.000000 |
| 43 | gill-color_o | 0.000000 |
116 rows × 2 columns
df_feat_imp_top10 = df_feat_importance_rf.sort_values('feature_importance', ascending=False).head(10)
df_feat_imp_top10
| features | feature_importance | |
|---|---|---|
| 27 | odor_n | 0.096636 |
| 35 | gill-size_b | 0.071668 |
| 57 | stalk-surface-above-ring_k | 0.070451 |
| 24 | odor_f | 0.069137 |
| 36 | gill-size_n | 0.053173 |
| 93 | ring-type_p | 0.039158 |
| 91 | ring-type_l | 0.035865 |
| 37 | gill-color_b | 0.035587 |
| 95 | spore-print-color_h | 0.033872 |
| 61 | stalk-surface-below-ring_k | 0.031121 |
These values were found standard-scaled to the range of 0 to 1. Even after a selection of the top 10 feature, as there was no sign of +ve or -ve from these feature importance values, we would not be able to gauge if these top 10 feature was positively or negatively affecting the mushroom class prediction. To solve this problem, the correlation table generated earlier in Part 2 was used as a reference.
# re-setup df to reflect which feature importance is positively or negatively affecting the mushroom class prediction
df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf = df_feat_imp_top10.merge(df_feature_correlation, how='inner', left_on='features', right_on='features')
df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf
| features | feature_importance | correlation_to_class | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | odor_n | 0.096636 | -0.785557 |
| 1 | gill-size_b | 0.071668 | -0.540024 |
| 2 | stalk-surface-above-ring_k | 0.070451 | 0.587658 |
| 3 | odor_f | 0.069137 | 0.623842 |
| 4 | gill-size_n | 0.053173 | 0.540024 |
| 5 | ring-type_p | 0.039158 | -0.540469 |
| 6 | ring-type_l | 0.035865 | 0.451619 |
| 7 | gill-color_b | 0.035587 | 0.538808 |
| 8 | spore-print-color_h | 0.033872 | 0.490229 |
| 9 | stalk-surface-below-ring_k | 0.031121 | 0.573524 |
By utilizing the +ve / -ve sign from the correlation_to_class column, it was then used as a reference sign to turn the original feature_important values into either a positive or negative value. WIth this method, the original weight of the feature important was retained and it was further enhanced to have an indication sign to show whether these features increased or decreased their importance affecting the class prediction.
df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf['revised_feature_importance'] = np.where(df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf['correlation_to_class']<0, -1*df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf['feature_importance'], df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf['feature_importance'])
df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf = df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf.sort_values(by='revised_feature_importance', ascending=False)
df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf
| features | feature_importance | correlation_to_class | revised_feature_importance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | stalk-surface-above-ring_k | 0.070451 | 0.587658 | 0.070451 |
| 3 | odor_f | 0.069137 | 0.623842 | 0.069137 |
| 4 | gill-size_n | 0.053173 | 0.540024 | 0.053173 |
| 6 | ring-type_l | 0.035865 | 0.451619 | 0.035865 |
| 7 | gill-color_b | 0.035587 | 0.538808 | 0.035587 |
| 8 | spore-print-color_h | 0.033872 | 0.490229 | 0.033872 |
| 9 | stalk-surface-below-ring_k | 0.031121 | 0.573524 | 0.031121 |
| 5 | ring-type_p | 0.039158 | -0.540469 | -0.039158 |
| 1 | gill-size_b | 0.071668 | -0.540024 | -0.071668 |
| 0 | odor_n | 0.096636 | -0.785557 | -0.096636 |
df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf.plot(x='features', y='revised_feature_importance', kind='barh', figsize=(12,6))
plt.title('Top 10 Feature for Mushroom Class Prediction based on Random_Forest_Classifier')
plt.show()
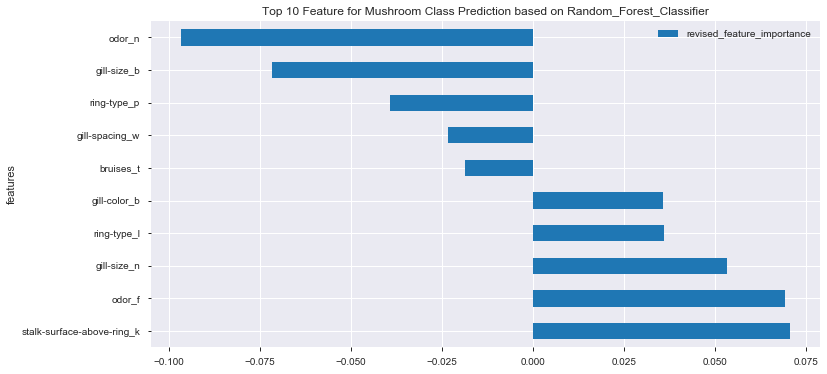
- No particular feature showing dominant effect on mushroom class prediction
- In general, combination of odor, gill-size, ring-type and stalk-surface demonstrated higher effects on final mushroom class prediction
4.3 Feature Importance derived from KNeighbors Classifier
As compared to Logistic RegressionCV and Random Forest Classifier, there’s no coefficient or feature importance that can be extracted easily from the trained model for Kneighbors Classifier. One way to quantitatively check which feature has greater impact is to perform n_features classification using ONE single feature at a time.
trained_model_kn = joblib.load('./pretrained_models/saved_model_kneighbors_classifier.sav')
features = data_test.columns
master_score_list = []
# iterate through each feature to check cross_val_score to find which features having higher score
for i, feature in enumerate(features):
data_single_feature = np.array(data_test.iloc[:, i]).reshape(-1, 1)
score_single_feature = cross_val_score(model_kn, data_single_feature, label_test, cv=3)
mean_score = np.mean(score_single_feature)
master_score_list.append(mean_score)
df_kNeighbors_feature_score = pd.DataFrame()
df_kNeighbors_feature_score['features'] = data_test.columns
df_kNeighbors_feature_score['cross_val_score_single_feature'] = master_score_list
df_kNeighbors_feature_score_top10 = df_kNeighbors_feature_score.sort_values('cross_val_score_single_feature', ascending=False).head(10)
df_kNeighbors_feature_score_top10
| features | cross_val_score_single_feature | |
|---|---|---|
| 27 | odor_n | 0.876126 |
| 24 | odor_f | 0.779325 |
| 61 | stalk-surface-below-ring_k | 0.763336 |
| 57 | stalk-surface-above-ring_k | 0.763333 |
| 36 | gill-size_n | 0.752266 |
| 35 | gill-size_b | 0.752266 |
| 21 | bruises_t | 0.735438 |
| 58 | stalk-surface-above-ring_s | 0.733388 |
| 37 | gill-color_b | 0.725599 |
| 93 | ring-type_p | 0.677935 |
Similar as Random Forest Classifier feature importanct study in Part 4.2, the cross validation score doesn’t have a +ve or -ve values. Therefore, the correlation_to_class column was merged in order to utilize its sign to convert the cross-val-score values.
# re-setup df to reflect which feature importance is carrying a postive or negative effect
df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn = df_kNeighbors_feature_score_top10.merge(df_feature_correlation, how='inner', left_on='features', right_on='features')
df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn
| features | cross_val_score_single_feature | correlation_to_class | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | odor_n | 0.876126 | -0.785557 |
| 1 | odor_f | 0.779325 | 0.623842 |
| 2 | stalk-surface-below-ring_k | 0.763336 | 0.573524 |
| 3 | stalk-surface-above-ring_k | 0.763333 | 0.587658 |
| 4 | gill-size_n | 0.752266 | 0.540024 |
| 5 | gill-size_b | 0.752266 | -0.540024 |
| 6 | bruises_t | 0.735438 | -0.501530 |
| 7 | stalk-surface-above-ring_s | 0.733388 | -0.491314 |
| 8 | gill-color_b | 0.725599 | 0.538808 |
| 9 | ring-type_p | 0.677935 | -0.540469 |
# utilize the correlation values to generate revised feature importances that reflect either having positive or negative effect
df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn['revised_feature_importance'] = np.where(df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn['correlation_to_class']<0, -1*df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn['cross_val_score_single_feature'], df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn['cross_val_score_single_feature'])
df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn = df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn.sort_values(by='revised_feature_importance', ascending=False)
df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn
| features | cross_val_score_single_feature | correlation_to_class | revised_feature_importance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | odor_f | 0.779325 | 0.623842 | 0.779325 |
| 2 | stalk-surface-below-ring_k | 0.763336 | 0.573524 | 0.763336 |
| 3 | stalk-surface-above-ring_k | 0.763333 | 0.587658 | 0.763333 |
| 4 | gill-size_n | 0.752266 | 0.540024 | 0.752266 |
| 8 | gill-color_b | 0.725599 | 0.538808 | 0.725599 |
| 9 | ring-type_p | 0.677935 | -0.540469 | -0.677935 |
| 7 | stalk-surface-above-ring_s | 0.733388 | -0.491314 | -0.733388 |
| 6 | bruises_t | 0.735438 | -0.501530 | -0.735438 |
| 5 | gill-size_b | 0.752266 | -0.540024 | -0.752266 |
| 0 | odor_n | 0.876126 | -0.785557 | -0.876126 |
df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn.plot(x='features', y='revised_feature_importance', kind='barh', figsize=(12,6))
plt.title('Top 10 Feature for Mushroom Class Prediction based on KNeighbors_Classifier')
plt.show()
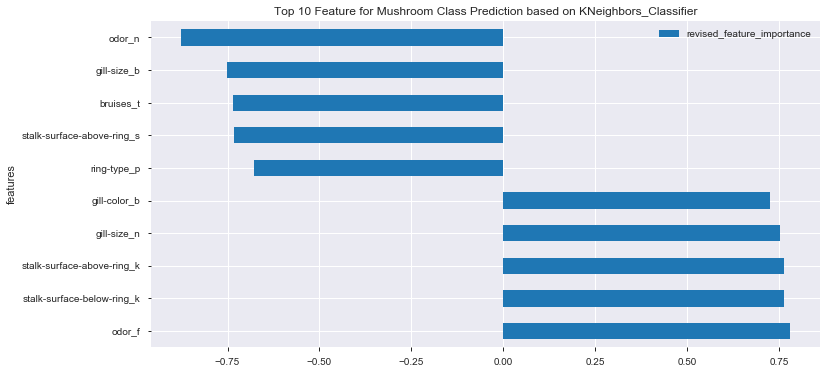
- No particular feature showing dominant effect on mushroom class prediction
- In general, combination of odor, gill-size and stalk-surface demonstrated higher effects on final mushroom class prediction
4.4 Common Top Feature across Difference Models
To find common top features that appear in all 3 models, simply iterate through features and feature-related dataframe
# find common top feature that appears in all 3 models
for feat in list(df_feat_coef_top10_lr['features']):
if (feat in list(df_feat_imp_correlation_top10_rf['features'])) and \
(feat in list(df_feat_score_correlation_top10_kn['features'])):
print(feat)
The print results showed common Top Features for all the evaluated models as follows:
odor_f
gill-size_b
odor_n
Part 5 : Conclusion
From the model preformance, all 3 evaluated models were found having good accuracy and F1 score. However, as these models were computed based on different algorithms, the feature importance extracted / identified from the models were therefore different. Consistency was observed in both odor and gill-size features in term of their influencing patterns :
- odor_f (foul) => positively influece the class prediction [ high tendency output as ‘poisonous’ ]
- gill-size_b (broad) and odor_n (none) => negatively influence the class prediction [ high tendency output as ‘edible’ ]
For highest safety and precautionary steps, it is still advisable to compare the mushroom class prediction for all 3 models. Only if all 3 models showing the same output predictions, the edibility of the mushroom is then best classified.
Extras : Deployment
For fast check on the models and its class prediction, you may check the link HERE